Hi all,
I created this page to store a repository of security and privacy techniques, apps and technologies. If you have good applications and/or practices please share with me and I will update this page with your input. (Securing WiFi Router at bottom of page)
General browsing/email info:
Email is not a secure method of communication. Refrain from including personal information such as SSNs, passwords, and banking information in your email correspondence.
Be suspicious of unsolicited emails with links or attachments.
Verify links before clicking. Use a URL expander tool such as https://urlex.org to verify a shortened link goes to the expected site.
Your password is yours alone. System administrators can set them as needed without user input and all requests for your password are an attempt to steal it.
If given the opportunity, choose a difficult to guess username.
Clean, up to date system
Make sure your system is completely up to date (e.g. OS, device drivers, virus definitions, applications, etc.) noting a single out of date application (e.g. pdf) can leave your system vulnerable.
Second, continually scan your system using your choice of anti-virus/anti-malware applications. In my Windows VMs, I use MS Security Essentials and Spybot Search and Destroy. Also, while we can ensure the integrity of our systems we cannot guarantee the integrity of our closest friends and family as their systems can get hacked and their compromised systems can send us
Also, beware and remain vigilant, while we can ensure the integrity of our systems we cannot guarantee the integrity of our closest friends and family as their systems can get hacked and their compromised systems can send us email.
Advice On Building A Better Password (from Information Week) Our first line of defense is to create strong, unique passwords for each site.
Ok, so I have 3 levels of passwords, 1) Throw away, 2) Secure and, 3) Ultimate Security
Construction a password so that it is different and unique across sites:
Construction methodology:
-
-
-
- Come up with two to three letters for the name of the application
- Follow this with a two to three-letter acronym
- Follow this by two to three numbers, which could be the year, a special date, or a special number.
- Add some symbols as separators
-
-
Process Example 1 Google:
-
-
-
- For Google begin with gOo (i.e. 3 letters and note I mix case)
- Choose a phrase “go Yankees,” so that it would be “gY.” again noting I mix case
- Choose date or some numeric sequence (ex. anniversary is Sept. 13, so => “913.”
- I will simply use hyphens but I recommend using mixed symbols like hyphens, asterisks, exclamations, etc.
- => gOo-Gy-913
-
-
Process Example 2 Yahoo:
-
-
-
- For Yahoo begin with yAh (i.e. 3 letters and note I mix case)
- Choose a phrase “go Yankees,” so that it would be “gY.” again noting I mix case
- Choose date or some numeric sequence (ex. anniversary is Sept. 13, so => “913.” F
- => yAh-gY-913
-
-
This kind of password doesn’t include any names, nicknames, or anything else easy for hackers to guess and it’s personalized.
Firewalls
We have covered firewalls (and their evolutionary generation functionality) so here’s how they should be configured.
Encryption
In a nutshell – encrypt everything that can be sensitive. My recommendation is that you do this at the OS level and Mac’s Filevault 2 is as good as it gets.
Should you wish to perform your encryption piecemeal, see: “How to Encrypt Anything” by PC World’s Alex Castle:
Safe Browsing
We need to continually and consciously be aware for our actions online and this includes Web based email. Make sure you see https in your browser’s location bar for any important transactions (see Ethics and Firesheep discussion). Do not click on unknown links, do not share information if you are uncomfortable and again question everything. For truly anonymous browsing you can use Onion Routing (TOR) but a CIS student just told me of a rumor the NSA is actually targeting TOR users and TOR traffic can be identified. Another anonymous browser is the Brave browser which has a built in VPN.
Verify links before clicking. Use a URL expander tool such as https://urlex.org to verify a shortened link goes to the expected site.
Anti-Virus
Not too much to say here other than use it. Mac and Linux are the least susceptivle to viruses for several reasons. Interestingly we have to increasingly be vigilant with our anti-virus software as Avast was found to be spying on its users.
I have a Mac so I use the free AVG. For my Windows VMs I use Microsoft Security Essentials and Spybot Search and Destroy. For my Linux VMs I don’t run anything and this is one of the beauties of Virtualization as I save a system state (snapshot) and should anything go awry I simply roll back and restore the clean state.
Note there are also desktop applications that monitor your Internet connections and these reveal how much communication (both good and bad) occur between you system/applications and the Internet. One such program is Little Snitch.
Anti-phishing/spoofing
Again, the onus is on us to consciously assess the credibility of online or Internet delivered communication. All communications should use the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Extended Validation (EV) as this encrypts sensitive data and anf facilitates Website authentication. Companies and individuals can be issued an Extended Validation (EV) SSL Certificate to display that they are a legitimate and this is identified by today’s browsers in the address bar.
There are various tools that allow users to verify sites and email addresses. Here are 2 examples:
WiFi Security
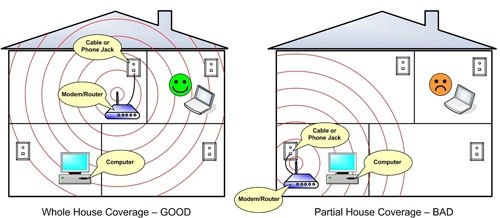
While this graphic is supposed to show how to get proper coverage within a house, look at coverage circles. The image on the right not only has poor transmission coverage in far corners of the house as the circle extends outside the house (i.e. WiFi eavesdropping). Now is there a window adjacent to the WiFi router as this will skew the circle outside the house even more as signals will pass through the window far easier than passing through walls.
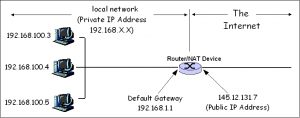
Simply adding a WiFi router can increase your security simply due to NAT and the fact that 192.168.x.x addresses are not publicly routable (i.e. if found on the Internet packets with 192.168.x addresses are dropped).
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) (from Wikipedia)
Originally Wi-Fi Simple Config, is a network security standard that attempts to allow users to easily secure a wireless home network but could fall to brute-force attacks if one or more of the network’s access points do not guard against the attack. With that let’s learn how to secure our network manually.
WiFi Router Configuration (manual config going beyond WiFi Protected Setup)
Start w/default factory settings and access router using ethernet port connection and IP address: 192.168.1.1
Router Name – nothing identifiable
SSID – nothing identifiable and don’t broadcast
Use WPA2 Personal Encription and choose a good password
Use a Wireless MAC filter and only allow your devices on your network (Use Mac/ios/Android system information or in Windows use cmd.exe and execute an ipconfig /a)
Disable wireless management
Disable remote management if possible
Use only HTTPs for management
Disable Ping if possible
Now for you gamers, if you enable a DMZ, please do so prudently.
Some What Is? answers for the WiFi Security recording above:
DDNS – Dynamic Domain Name System from Wikipedia
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) is a method of automatically updating a name server in the Domain Name System (DNS), often in real time, with the active DNS configuration of its configured hostnames, addresses or other information. The term is used to describe two different concepts. At the administration levels of the Internet, “dynamic DNS updating” refers to systems that are used to update traditional DNS records without manual editing. These mechanisms are explained in RFC 2136, and use the TSIG mechanism to provide security. Another kind of dynamic DNS permits lightweight and immediate updates to its local database, often using a web-based mechanism. It is used to resolve a well-known domain name to an IP address that may change frequently. It provides a persistent addressing method for devices that change their location or configuration.
uPnP – Universal Plug and Play – Wikipedia
Universal Plug and Play is a set of networking protocols that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices to seamlessly discover each other’s presence on the network and establish functional network services for data sharing
Short Guard Interval – from Wikipedia
In telecommunications, guard intervals are used to ensure that distinct transmissions do not interfere with one another. These transmissions may belong to different users (as in TDMA) or to the same user (as in OFDM). The purpose of the guard interval is to introduce immunity to propagation delays, echoes and reflections, to which digital data is normally very sensitive.
SPI Mode – Stateful Packet Inspection as previously introduced.
Multicast Streams – About multicast streaming – TechNet – Microsoft
Multicast streaming is a one-to-many relationship between a Windows Media server and the clients receiving the stream.
Port Range Forwarding – from Linksys
Port range forwarding is done so the data for Internet applications can pass through the firewall of the router or gateway. An example of an application port is port 25 which is assigned for email or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
Port Range Triggering – from Wikipedia
Port triggering is a configuration option on a NAT-enabled router that allows a host machine to dynamically and automatically forward a specific port back to itself. Port triggering opens an incoming port when your computer is using a specified outgoing port for specific traffic.
Closing advice/information
Free Wi-Fi may come with a cost: Some free or public Wi‑Fi connections may intercept your sensitive credentials. Only connect to networks you know and trust.
Lock it up: Keep your phone safe by enabling it to automatically lock after a certain period of time. Ensure your password is strong and not easy to guess, or use Touch ID to balance security and convenience.
Steer clear of malicious apps: Avoid installing applications from unknown third-party app stores. Find anti-malware solutions on the App Store® or Google Play™.